5 Ways to Master Business Risk Transfer: A Strategic Guide for Success
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to 5 Ways to Master Business Risk Transfer: A Strategic Guide for Success. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
5 Ways to Master Business Risk Transfer: A Strategic Guide for Success

Business risk is an unavoidable reality. From economic downturns to natural disasters, unforeseen events can disrupt operations, damage reputation, and erode profitability. While some risks can be mitigated through internal controls and careful planning, others are simply too large or unpredictable to manage effectively. This is where risk transfer comes in.
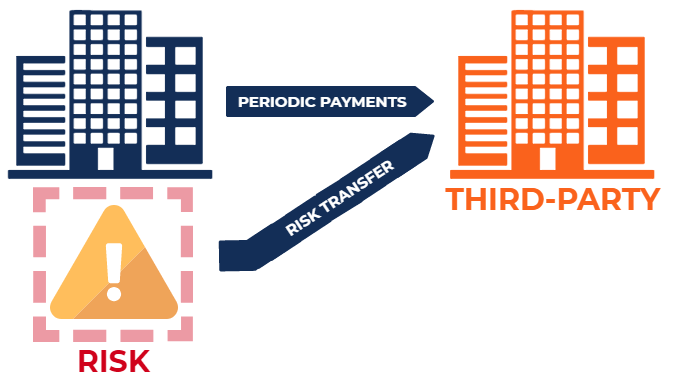
Risk transfer, also known as risk shifting, is a strategic approach that involves transferring the financial burden of certain risks to a third party. By strategically transferring risks, businesses can protect their bottom line, maintain financial stability, and focus on their core competencies.
This article will explore five key strategies for mastering business risk transfer, providing a comprehensive guide for businesses of all sizes.
1. Insurance: The Cornerstone of Risk Transfer
Insurance is the most common and widely understood form of risk transfer. It involves paying a premium to an insurance company in exchange for financial protection against specific risks. Insurance policies can cover a wide range of potential losses, including:
- Property damage: Protecting buildings, equipment, and inventory against fire, theft, natural disasters, and other perils.
- Liability: Providing financial protection against lawsuits arising from accidents, negligence, or product defects.
- Business interruption: Covering lost income and expenses incurred due to a temporary shutdown of operations.
- Cybersecurity: Protecting against data breaches, cyberattacks, and other digital threats.
Choosing the right insurance coverage is crucial. Businesses should carefully assess their risk profile and identify the most critical areas to insure. Working with a qualified insurance broker can help businesses navigate the complex world of insurance options and secure the most appropriate coverage.
2. Contracts: Shifting Risk through Agreements
Contracts can be powerful tools for transferring risk. By carefully drafting contract terms, businesses can shift the responsibility for specific risks to their partners, suppliers, or customers. Some common examples of risk transfer through contracts include:
- Indemnification clauses: These clauses require one party to compensate another party for losses caused by their actions or omissions.
- Warranties: Manufacturers or suppliers can provide warranties that guarantee the quality or performance of their products or services, assuming the financial burden for any defects or failures.
- Hold harmless agreements: These agreements protect one party from liability for losses caused by the other party’s actions.
- Exculpatory clauses: These clauses limit or eliminate liability for certain types of risks, such as accidents or injuries occurring on a business’s premises.

It is crucial to consult with legal counsel to ensure that contract terms effectively transfer risk and comply with applicable laws and regulations.
3. Hedging: Mitigating Financial Risk
Hedging is a financial strategy used to reduce the financial impact of unfavorable price fluctuations in commodities, currencies, or interest rates. Businesses can use various hedging instruments, such as futures contracts, options, and swaps, to lock in prices or rates and protect themselves from potential losses.
For example, a manufacturing company that relies heavily on oil as a raw material can hedge against rising oil prices by purchasing oil futures contracts. This allows them to buy oil at a predetermined price, regardless of future market fluctuations.
Hedging requires careful planning and expertise. Businesses should consult with financial professionals to develop appropriate hedging strategies that align with their specific risk profile and financial goals.
4. Outsourcing: Sharing Risk with Third-Party Providers
Outsourcing certain business functions can be an effective way to transfer risk. By engaging third-party providers, businesses can shift the responsibility for managing specific risks to specialized experts.
For example, a company can outsource its IT infrastructure to a cloud service provider, transferring the risk of hardware failures, security breaches, and maintenance costs. Similarly, businesses can outsource payroll processing, logistics, or customer service to external companies, reducing their own operational risks.
Choosing reputable and reliable outsourcing partners is essential. Businesses should carefully evaluate the financial stability, expertise, and track record of potential providers to ensure that they can effectively manage the transferred risks.
5. Reinsurance: Spreading Risk across Multiple Insurers
Reinsurance is a form of insurance for insurance companies. It allows primary insurers to transfer a portion of their risk to other insurers, known as reinsurers. Reinsurance can help insurers manage large or complex risks that they may not be able to handle alone.
Businesses can indirectly benefit from reinsurance by working with insurers who have access to reinsurance markets. This can provide broader coverage and greater financial stability in case of catastrophic events.
Benefits of Effective Risk Transfer
Mastering risk transfer offers numerous benefits for businesses:
- Improved financial stability: By transferring risk, businesses can protect their assets and cash flow from unexpected losses.
- Reduced operational disruptions: Risk transfer can help minimize disruptions to operations caused by unforeseen events.
- Enhanced competitive advantage: By managing risk effectively, businesses can focus on their core competencies and gain a competitive edge.
- Increased investor confidence: Investors are more likely to invest in businesses that have a robust risk management strategy in place.
Considerations for Effective Risk Transfer
While risk transfer can be a powerful tool, it’s crucial to consider the following factors:
- Cost-benefit analysis: Evaluate the potential benefits of risk transfer against the associated costs, such as insurance premiums or contract fees.
- Legal and regulatory compliance: Ensure that all risk transfer strategies comply with applicable laws and regulations.
- Transparency and communication: Maintain open communication with stakeholders about the risks being transferred and the strategies employed.
- Ongoing monitoring and evaluation: Regularly review and adjust risk transfer strategies to ensure their effectiveness and alignment with changing business needs.
Conclusion
Mastering business risk transfer is essential for achieving long-term success. By strategically transferring risks to third parties, businesses can protect their bottom line, maintain financial stability, and focus on their core competencies. By carefully considering the various risk transfer strategies outlined in this article, businesses can build a robust risk management framework that mitigates potential losses and paves the way for sustainable growth.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into 5 Ways to Master Business Risk Transfer: A Strategic Guide for Success. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
google.com


