5 Crucial Elements of Unbreakable Business Legal Contracts
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to 5 Crucial Elements of Unbreakable Business Legal Contracts. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
5 Crucial Elements of Unbreakable Business Legal Contracts
In the fast-paced world of business, where deals are struck, partnerships forged, and ventures launched, legal contracts are the bedrock of security and stability. They provide a clear framework for outlining the rights, obligations, and responsibilities of all parties involved, ensuring that everyone understands their roles and expectations.
However, crafting an effective business contract goes beyond simply drafting a document. It requires careful consideration of numerous factors, including the specific nature of the agreement, the applicable laws, and the potential risks involved.
This article delves into five crucial elements that form the foundation of unbreakable business legal contracts, empowering you to navigate the complexities of legal agreements with confidence.
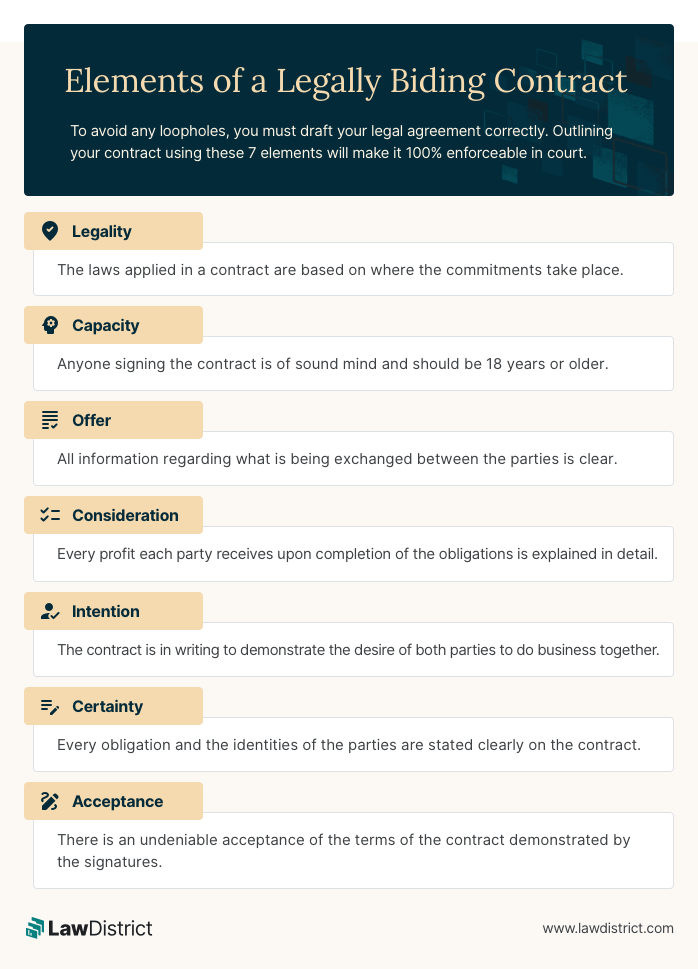
1. Clear and Concise Language:
The foundation of any effective contract lies in its clarity and conciseness. Ambiguity can lead to misunderstandings, disputes, and ultimately, costly legal battles.
Key Principles:
- Avoid legalese: While legal terminology may seem impressive, it often creates confusion for parties unfamiliar with the nuances of legal language. Opt for plain English that is easily understood by all involved.
- Define key terms: Any term with a specific meaning within the context of the agreement should be explicitly defined. This avoids misinterpretations and ensures everyone is on the same page.
- Use precise language: Avoid vague or general statements. Instead, use specific language to clearly define the scope of the agreement, the obligations of each party, and the consequences of breaching the contract.
Example:
Instead of stating, "The parties agree to cooperate in good faith," consider specifying the nature of the cooperation required, such as, "The parties agree to share information related to marketing campaigns and provide mutual support in sales efforts."
2. Comprehensive Scope of Agreement:
A well-structured contract should cover all aspects of the business relationship, leaving no room for ambiguity or future disputes.

Essential Components:
- Purpose and subject matter: Clearly define the purpose of the agreement and the specific subject matter it covers. This sets the foundation for understanding the scope of the contract.
- Parties involved: Identify all parties involved in the agreement, including their legal names and addresses. This ensures proper identification and facilitates communication.
- Terms and conditions: Outline the specific terms and conditions of the agreement, including timelines, deliverables, payment terms, and any other relevant details.
- Termination clause: Specify the conditions under which the agreement can be terminated, including notice periods, grounds for termination, and consequences of termination.
Example:
A contract for software development should not only outline the deliverables but also include provisions for intellectual property rights, confidentiality, warranties, and liability limitations.
3. Binding and Enforceable Provisions:
For a contract to be truly effective, it must be legally binding and enforceable. This requires incorporating specific provisions that meet the legal requirements of the jurisdiction where the contract is executed.
Key Considerations:
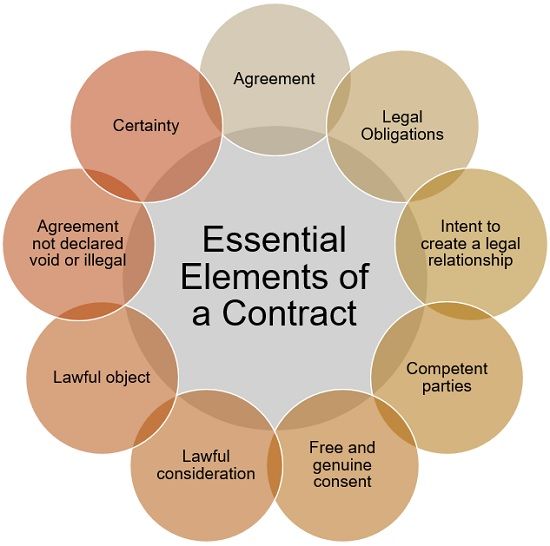
- Offer and acceptance: The contract must demonstrate a clear offer and acceptance of the terms by all parties involved. This establishes the basis for a legally binding agreement.
- Consideration: Each party must provide something of value in exchange for the promises made in the contract. This can be a tangible benefit, a service, or a promise to perform a specific action.
- Capacity to contract: All parties must have the legal capacity to enter into a contract. This means they must be of legal age, mentally competent, and not under duress or undue influence.
- Legality: The subject matter of the contract must be legal and not violate any applicable laws or regulations.
Example:
A contract for the sale of illegal substances would be void and unenforceable as it violates the law.
4. Risk Mitigation and Liability Management:
Business relationships inevitably involve risks. A well-crafted contract should include provisions that effectively mitigate these risks and manage potential liabilities.
Essential Clauses:
- Warranties and indemnities: These clauses specify the warranties provided by each party and the extent to which they are responsible for damages caused by their actions or omissions.
- Limitation of liability: This clause sets limits on the financial liability of each party for breaches of contract or other incidents.
- Dispute resolution: This clause outlines the process for resolving disputes that may arise between the parties, including mediation, arbitration, or litigation.
- Force majeure: This clause addresses unforeseen events, such as natural disasters or government regulations, that may prevent a party from fulfilling its obligations under the contract.
Example:
A contract for a construction project should include clauses addressing potential delays, defects in materials, and liability for accidents on the construction site.
5. Effective Communication and Record-Keeping:
Maintaining clear communication and meticulous record-keeping are essential for ensuring the smooth execution and enforcement of any business contract.
Key Practices:
- Regular communication: Establish clear communication channels for all parties involved, including methods for exchanging information, resolving issues, and providing updates.
- Detailed documentation: Document all important interactions, agreements, and modifications to the contract. This includes emails, meeting minutes, and any other relevant records.
- Version control: Maintain a clear record of all contract versions, including dates of changes and the reasons for revisions. This ensures transparency and accountability.
Example:
A contract for a joint venture should include provisions for regular meetings, detailed progress reports, and a system for managing and archiving all relevant documents.
Conclusion:
Crafting unbreakable business legal contracts requires a meticulous approach, encompassing clarity, comprehensiveness, enforceability, risk mitigation, and effective communication. By understanding and incorporating these five crucial elements, businesses can establish a solid foundation for their agreements, minimizing the risk of disputes and ensuring the successful execution of their business objectives.
Remember:
While this article provides a general overview of key elements, it is essential to consult with legal professionals to ensure your contracts are tailored to the specific needs of your business and comply with all applicable laws and regulations.
By investing in professional legal guidance and taking the time to create robust and comprehensive contracts, businesses can protect their interests, foster trust, and pave the way for sustainable and successful partnerships.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into 5 Crucial Elements of Unbreakable Business Legal Contracts. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
google.com


